Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD) is a complex mental health condition that impacts various aspects of individuals’ lives. It involves an inflated sense of self-importance, an insatiable need for admiration, and a lack of empathy.
In this blog post, we will explore different aspects of narcissistic personality disorder, including the nine traits, five main habits, indicators of narcissism, as well as the causes, progression, diagnosis, available tests for NPD and treatments.
Nine Traits of a Narcissist
Narcissistic personality disorder is identified by specific traits, although not all narcissists exhibit each trait to the same degree. Here are the nine common characteristics:
- Exaggerated Self-Importance: Narcissists often believe they are superior to others.
- Fantasies of Power and Success: They harbor unrealistic dreams of limitless achievements and influence.
- Constant Need for Admiration: Narcissists seek constant validation, attention, and admiration.
- Sense of Entitlement: They believe they deserve special treatment without reciprocation.
- Lack of Empathy: Narcissists struggle to understand and relate to others’ emotions.
- Manipulative Behavior: They exploit and manipulate others to meet their own needs.
- Envy of Others: Narcissists may experience envy and resentment towards others’ accomplishments.
- Arrogance and Haughtiness: They exhibit an arrogant and superior attitude.
- Fragile Self-Esteem: Beneath their grandiose facade, narcissists often possess fragile self-esteem and are easily hurt by criticism.
Five Main Habits of a Narcissist
In addition to the aforementioned traits, narcissists tend to display specific habits in their interactions and relationships. Here are five primary habits associated with narcissistic behavior:
- Manipulation: Narcissists are skilled manipulators, using charm and deceit to control and exploit others.
- Gaslighting: They manipulate situations to make others doubt their perceptions, memories, and sanity.
- Avoiding Accountability: Narcissists rarely take responsibility for their actions, often deflecting blame onto others.
- Disregarding Boundaries: They struggle to respect personal boundaries, intruding on privacy and emotions.
- Discarding and Devaluing: Narcissists may discard or devalue individuals who no longer serve their needs or challenge their superiority.
Recognizing Narcissistic Traits in Others
Identifying narcissistic traits in individuals can be challenging, as the degree of narcissism may vary. However, several signs may indicate narcissistic tendencies:
- Excessive Self-Centeredness: They prioritize their own needs and desires, displaying minimal empathy.
- Insatiable Need for Attention: Narcissists constantly seek admiration, attention, and validation.
- Lack of Empathy: They struggle to understand and empathize with others’ emotions and experiences.
- Manipulative Behavior: They employ manipulation and deception to control and exploit others.
- Difficulty Accepting Criticism: Narcissists often react defensively or angrily to criticism as it threatens their fragile self-esteem.
Understanding the causes, progression, diagnosis, and available tests related to narcissistic personality disorder provides crucial insights. Let’s explore each of these aspects individually:
Causes of Narcissistic Personality Disorder
The exact causes of narcissistic personality disorder are still under investigation.
The University of Chicago Medicine spearheaded research indicating that individuals with Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD) exhibit heightened levels of oxidative stress in their bloodstream, and this condition is additionally linked to heightened sensitivity in interpersonal relationships.
It is likely that a combination of factors which contributes to the development of NPD. These factors include:
Genetics
Research suggests that genetics may play a role, with certain genetic variations potentially increasing susceptibility to NPD
Environment
Upbringing and early-life experiences can shape personality. Childhood trauma, neglect, excessive pampering, or inconsistent parenting styles may contribute to the development of narcissistic traits.
Psychological Factors
Low self-esteem or feelings of inadequacy can contribute to the development of narcissistic personality disorder. Individuals may adopt narcissistic defense mechanisms to protect themselves from vulnerability.
Stages of Narcissistic Personality Disorder
Narcissistic personality disorder is not characterized by distinct stages but rather by a progressive pattern of behaviors and symptoms. However, understanding the general trajectory of the disorder can be helpful:
Emergence of Narcissistic Traits
Narcissistic traits become noticeable during adolescence or early adulthood. Individuals may exhibit self-centeredness, a need for admiration, and a lack of empathy.
Consolidation of Narcissistic Behavior
As narcissistic traits intensify, individuals may engage in manipulation, exploitation, and entitlement. They become increasingly invested in maintaining their grandiose self-image.
Escalation of Narcissistic Patterns
Without intervention, narcissistic behavior escalates, leading to a disregard for others’ boundaries, ongoing interpersonal conflicts, and difficulties in forming and maintaining healthy relationships.
Impact on Well-Being
Over time, the consequences of narcissistic behavior negatively affect various aspects of an individual’s life, including relationships, work or academics, and overall emotional well-being.
Diagnosis of Narcissistic Personality Disorder
A comprehensive evaluation by a qualified mental health professional is necessary to diagnose narcissistic personality disorder. The diagnostic process generally involves:
Clinical Assessment
A mental health professional conducts a thorough clinical assessment, gathering information on personal and family history, current symptoms, and functional impairment.
Diagnostic Criteria
Referring to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), the clinician identifies specific criteria for narcissistic personality disorder. These criteria include enduring and significant narcissistic traits causing distress or impairment in multiple life areas.
Observation and Interview
The mental health professional observes the individual’s behavior, attitudes, and interpersonal interactions during the assessment. Structured interviews may also be used for detailed information gathering.
Available Tests for Narcissistic Personality Disorder
While no specific medical tests exist for diagnosing narcissistic personality disorder, mental health professionals may employ standardized psychological assessments to support the diagnostic process. These assessments provide additional information. Some commonly used tests include:
Narcissistic Personality Inventory (NPI)
This self-report questionnaire measures narcissistic traits. Individuals rate several statements based on their level of agreement or disagreement.
Millon Clinical Multiaxial Inventory (MCMI-IV)
The MCMI-IV assesses various psychological disorders, including narcissistic personality disorder. It provides insights into an individual’s personality patterns and clinical features.
Personality Assessment Inventory (PAI)
This self-report inventory evaluates a wide range of personality and psychopathology constructs. It offers valuable information on narcissistic traits and their impact on functioning.
These tests, combined with clinical judgment and comprehensive assessment, contribute to a thorough diagnosis of narcissistic personality disorder.
Understanding narcissistic personality disorder involves recognizing its traits, identifying common habits, and being aware of signs in others.
Additionally, knowledge of the causes, progression, diagnosis, and available tests provides valuable insights into this complex condition.
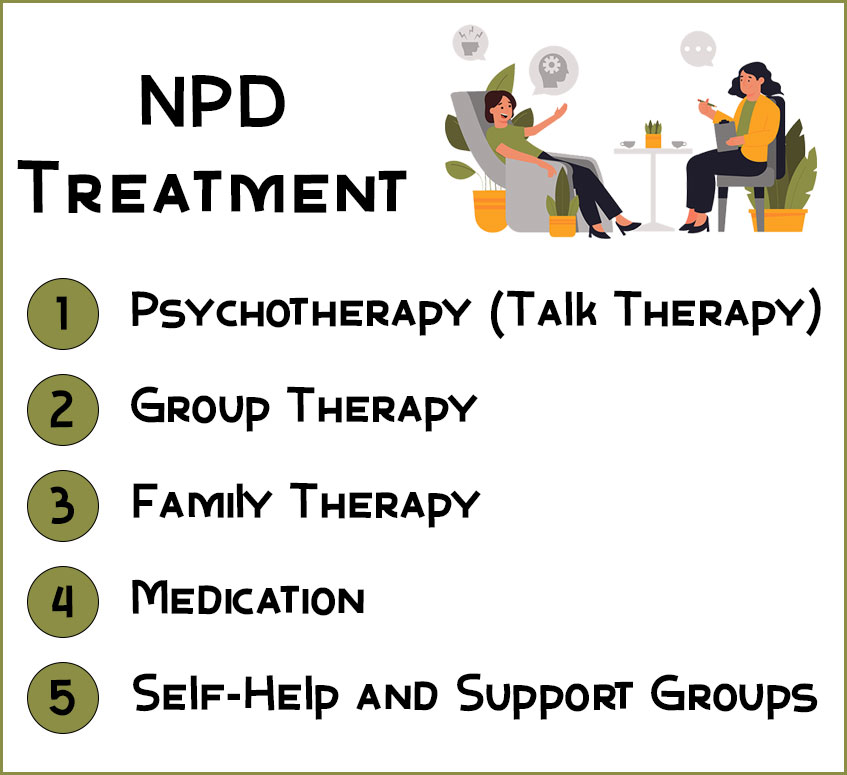
Narcissistic Personality Disorder Treatment
Addressing narcissistic personality disorder (NPD) presents challenges due to its complex nature.
Individuals with NPD may have limited self-awareness and resistance towards seeking help. However, with the guidance of qualified mental health professionals and a commitment to personal growth, various therapeutic approaches can be beneficial.
It’s important to note that treatment outcomes can vary, and a tailored approach is necessary. The following are commonly used treatments for narcissistic personality disorder:
Psychotherapy (Talk Therapy)
Psychotherapy is the primary treatment for NPD. Different therapeutic approaches can be effective, including:
- Psychodynamic Therapy: This therapy explores unconscious processes and early life experiences that contribute to NPD. It enhances self-awareness, addresses emotional conflicts, and promotes personal growth.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps individuals identify and challenge dysfunctional thoughts and behaviors associated with narcissistic traits. It develops adaptive coping strategies, improves interpersonal skills, and encourages empathy and self-reflection.
- Schema Therapy: This therapy focuses on negative patterns of thinking and behavior underlying NPD. It helps individuals develop healthier coping mechanisms, cultivate self-compassion, and foster fulfilling relationships.
Group Therapy
Group therapy provides a beneficial setting for individuals with NPD. Interacting with others who share similar experiences promotes learning and self-reflection. It fosters empathy, interpersonal skills, and healthier relationship dynamics.
Family Therapy
Involving family members in therapy can be helpful, particularly when dysfunctional family dynamics contribute to NPD. Family therapy improves communication, addresses conflicts, and promotes healthier relationship patterns.
Medication
While there is no medication specifically for NPD, medications may be prescribed to manage co-occurring conditions such as depression, anxiety, or mood disorders. Treating these symptoms can enhance overall well-being.
Self-Help and Support Groups
Engaging in self-help strategies and participating in support groups provides additional support for individuals with NPD. These avenues offer non-judgmental spaces to share experiences, learn from others, and develop coping strategies.
It’s important to recognize that progress in treating narcissistic personality disorder may be slow and require long-term commitment. Individuals with NPD may face challenges in self-reflection and change. However, with consistent effort, therapy, and a supportive environment, progress can be made in managing symptoms and developing healthier relationships.
Working with qualified mental health professionals experienced in treating personality disorders is crucial. They can tailor the treatment approach to each individual’s unique needs and provide guidance throughout the therapeutic process.
Whether you suspect someone you know may be struggling with narcissism or you recognize these traits within yourself, professional support can lead to a deeper understanding and potential paths to personal growth and healing.