Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the primary psychoactive compound in marijuana, responsible for the euphoric “high” that users experience.
If you’re wondering how long THC and weed stay in your system, including your bloodstream, urine, and hair, you’ve come to the right place.
Below you’ll find the factors affecting the duration of THC presence and provide insights into different marijuana tests.
Understanding THC and Its Persistence
THC quickly transforms into metabolites that are stored in your body fat for up to two weeks after consumption. However, the exact time it takes for weed, THC, or its metabolites to exit your system varies from person to person.
Factors like frequency of use, metabolism, body composition, and genetics all play a role. Some marijuana tests can detect THC even months after use.
The Complex Nature of Cannabis
Cannabis, known by various names like weed, pot, ganja, Mary Jane, herb, or marijuana, remains a subject of controversy due to its legal status and medicinal properties.
While some advocate for its legalization, others are concerned about its potential for addiction and its connection to stronger substances.
According to the World Health Organization, cannabis ranks as one of the most widely cultivated, trafficked, and abused illicit drugs globally.
With approximately 150 million users and a significant percentage of all drug seizures attributed to marijuana, it’s a topic of significant interest.
How Long Does Marijuana Stay in Your System?
Now, let’s address the burning questions: How long does marijuana stay in your blood, urine, or hair?
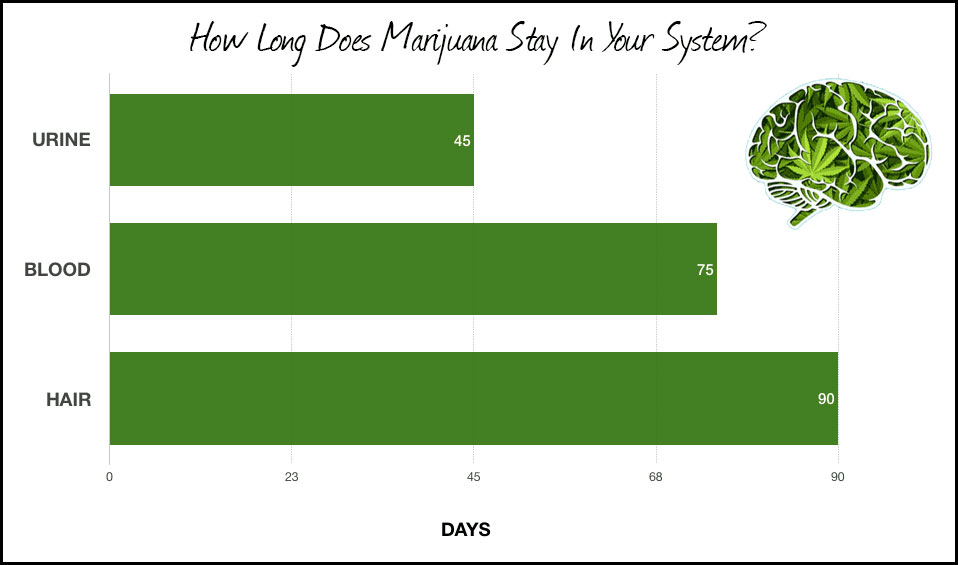
- Urine: Marijuana can be detected in urine for up to 45 days, with some cases extending to 90 days for heavy users.
- Blood: While blood tests can detect THC within minutes of use, the detection window may extend to several days.
- Hair: THC metabolites can remain trapped in hair follicles for up to 90+ days as hair grows.
Factors Influencing Duration
Several factors influence how long marijuana lingers in your system:
- Duration/Frequency of Use: Chronic users metabolize THC slower than occasional users.
- Body Fat: THC metabolites are fat-soluble and can accumulate in fat cells.
- Metabolism: Individuals with faster metabolism eliminate THC faster.
- Genetics: Genetics affect how the body metabolizes and eliminates THC.
- Type/Strain of Marijuana: Different strains contain varying THC levels.
- Test Sensitivity: Tests with lower cutoff levels can detect THC for longer periods.
Detection Windows for Different Tests
Marijuana can be detected using various screening tests, each with its detection window:
- Urine: Most common, detecting marijuana up to 13-45 days.
- Blood: Quick detection within minutes, possibly up to several days.
- Hair: Traces of THC metabolites detectable for up to 90+ days.
- Saliva/Sweat: Less common, shorter detection windows.
Accuracy of Urine Tests
Modern urine tests are highly accurate, comprising immunoassay tests followed by gas chromatograph mass spectrometry. Drinking water or using detox kits may not eliminate THC entirely, and tampering with urine samples is detectable.
Passing a Urine Test
The only surefire way to pass a urine test is to abstain from marijuana before testing. No quick fixes or detox kits can guarantee a clean result.
Driving Under the Influence
It’s important to note that driving under the influence of marijuana is illegal, even in regions where it’s legalized. Marijuana can impair your driving for up to 3 hours after use, leading to slower reactions.
Second-Hand Smoke
The risk of testing positive for marijuana as a second-hand smoker is low unless exposed to a concentrated, unventilated environment for extended periods.
While there’s no definitive answer to how long weed stays in your system, it’s clear that THC can persist long after the high wears off.
If you find yourself frequently searching for “how long does marijuana stay in the system,” it may be time to reconsider your habits. Relying on at home detox kits or tampering with test samples won’t address the underlying issue.